The Center for Bioinformatics and Intelligent Medicine team published a paper in Briefings in Bioinformatics
September 07,2022 Editor:Centre for Bioinformatics and Intelligent Medicine
The lab team published “SCDD: a novel single-cell RNA-seq imputation method with diffusion and denoising ” in Briefings in Bioinformatics.
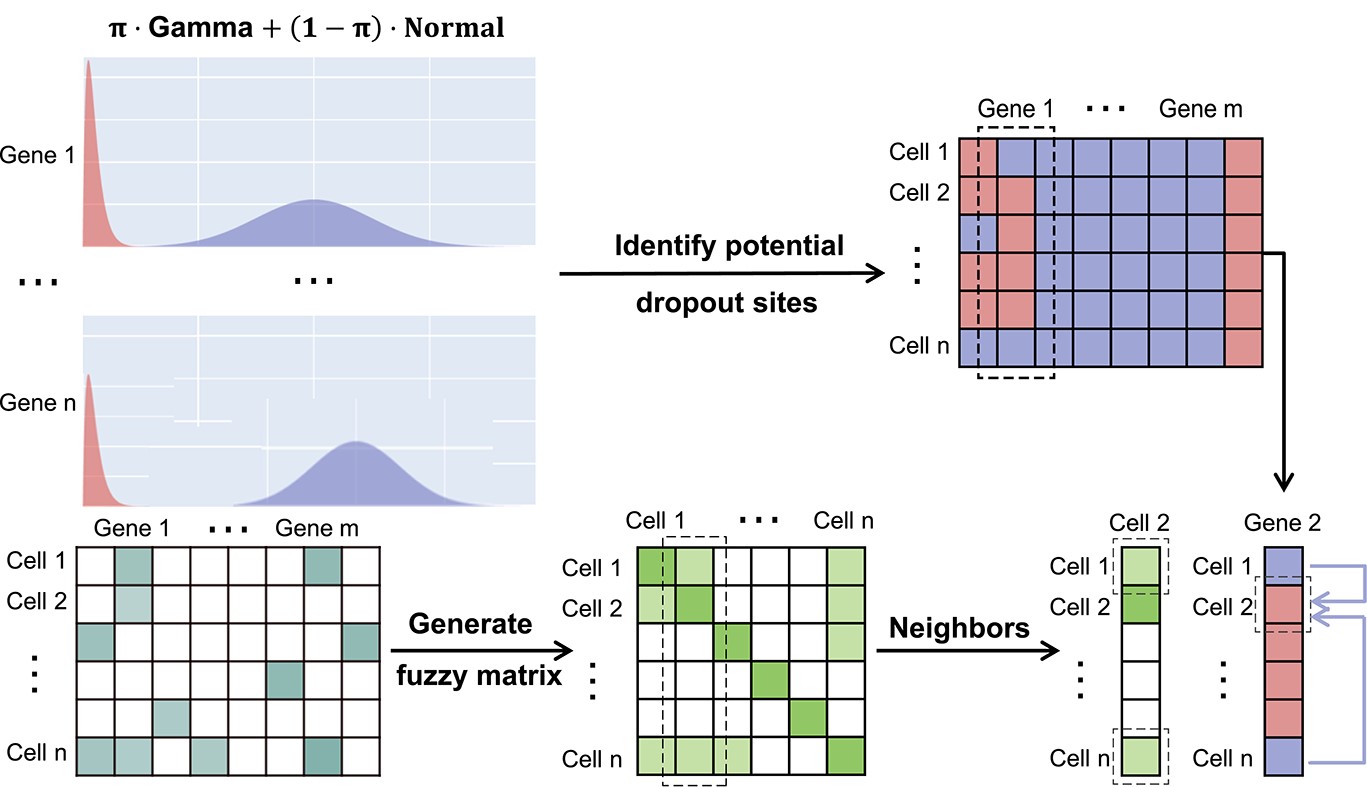
Single-cell transcriptome sequencing is a technique that can measure transcriptome expression on a cellular basis. Currently, scRNA-seq suffers from some limitations, for example, it may generate a large number of low expression values due to the relatively low mRNA expression, the insufficient capture efficiency or the low sequencing depth. In fact, these low expression values in scRNA-seq data are not the results of lacking in actual expressions, which are referred to as the dropout events.
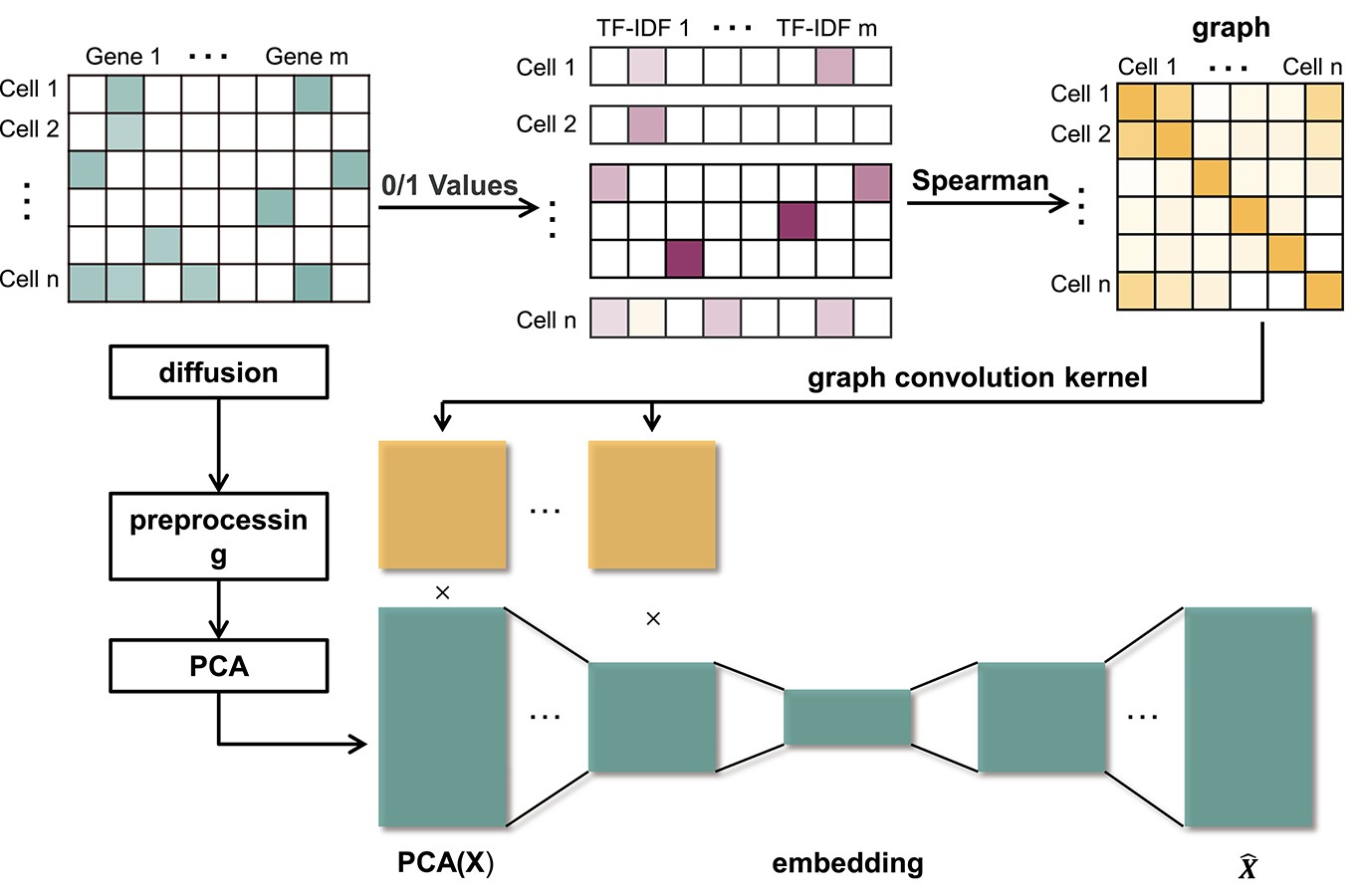
We propose a method called SCDD to impute dropout events and verify its advantages over traditional methods. SCDD consists of two stages, diffusion stage and denoising stage. In the diffusion stage, mixed models of a Gamma distribution and a Normal distribution are firstly developed for each gene to identify the potential dropout sites. At the same time, a fuzzy matrix identifying neighbours of each cell is generated. For each identified potential dropout site, the expression values of its neighbours diffuse to this site. These diffused expression values are then used as the input of the NN in the denoising stage. In addition, 0/1 values are generated based on whether the scRNA-seq expression values are bigger than 0. After that, the graph used in GCN is generated, where each cell is a node, and the Spearman correlation of each pair of cells is the weight of the edge associated with this pair. Then, at each layer of the GCN, SCDD generates superposition values using the matrix multiplication. Finally, SCDD restores the preprocessed diffused expression from the embedding and generates the imputation results.