The Center for Bioinformatics and Intelligent Medicine team published a paper in Briefings in Bioinformatics
July 30,2023 Editor:Centre for Bioinformatics and Intelligent Medicine
The lab team published “HiBrowser: An Interactive and Dynamic Browser for Synchronous Hi-C Data Visualization” in Briefings in Bioinformatics.
The high-throughput Chromosome Conformation Capture (Hi-C) sequencing technology provides a highly promising approach for generating high-quality multi-omics data and conducting comparative multi-omics analyses. Its widespread application has greatly revolutionized researchers' understanding of genome organization. Studies have demonstrated that the three-dimensional (3D) organization of the mammalian genome plays a crucial role in gene regulation. By folding and integrating regulatory activities within the same structural domains, it facilitates the regulation of transcriptional processes.
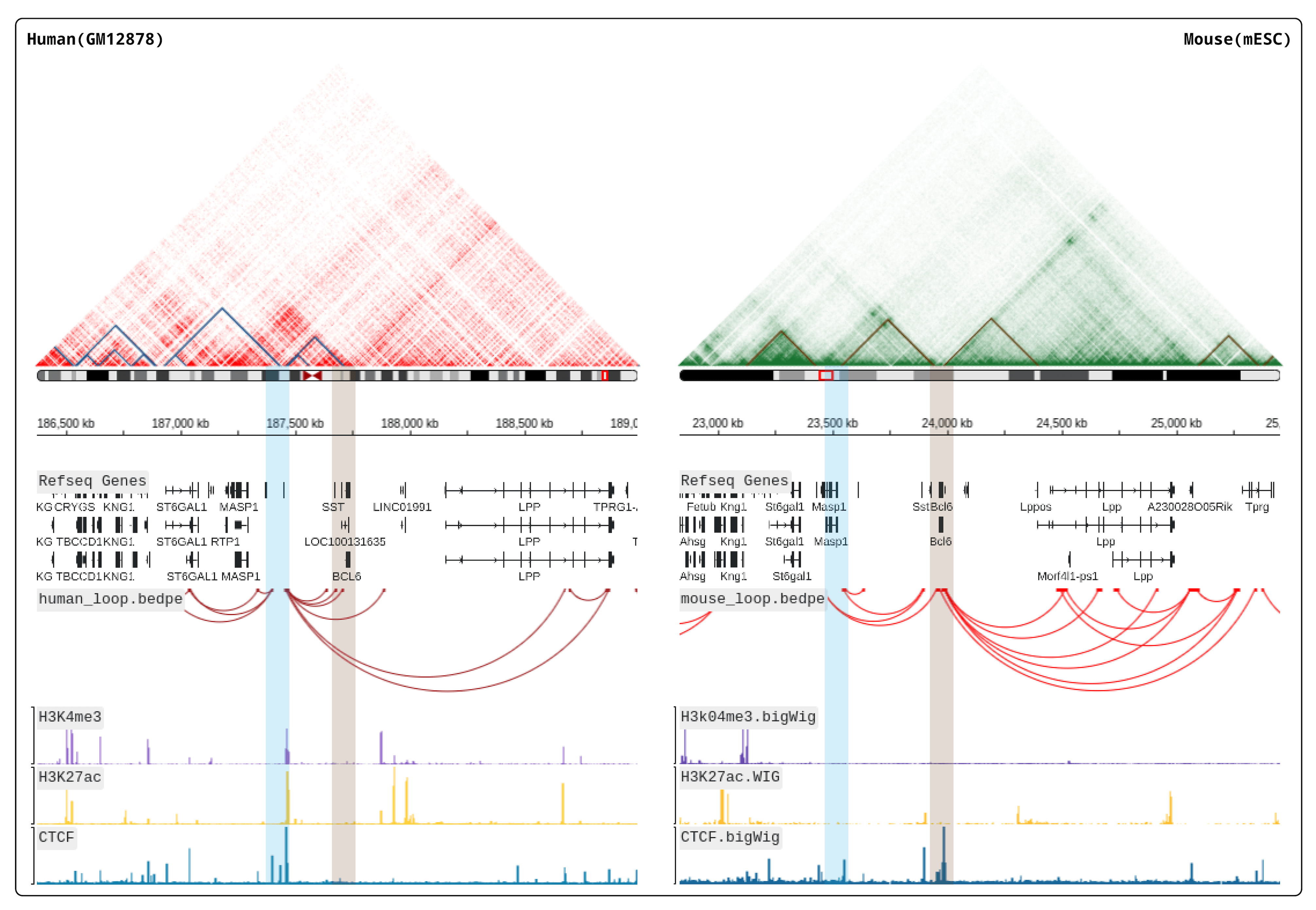
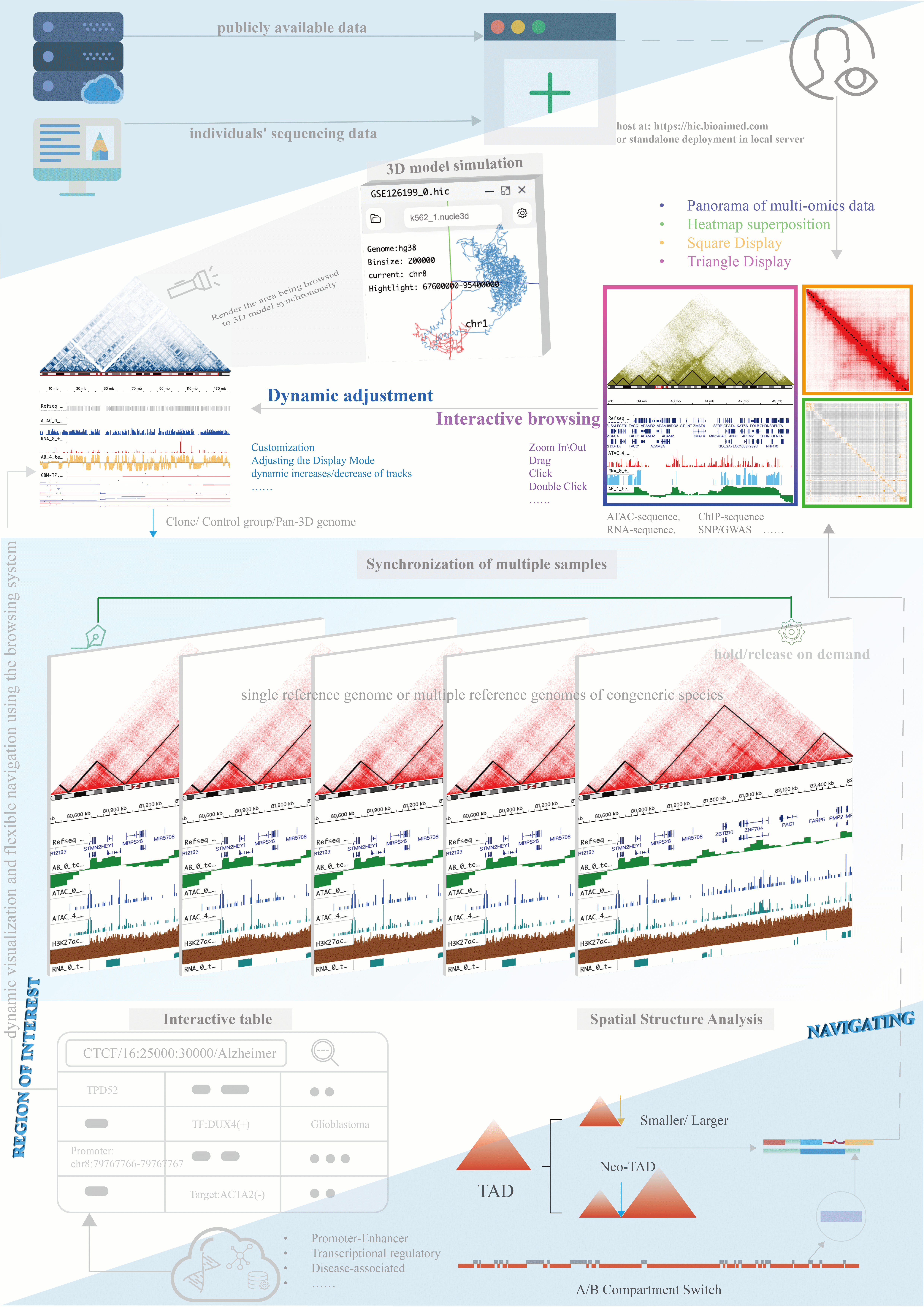
HiBrowser is an out-of-the-box, interactive and dynamic browser that allows for flexible and dynamic reconstruction of custom annotation tracks. Users can use HiBrowser to browse Hi-C heatmaps and multi-omics annotation tracks synchronously, providing a convenient online visualization platform for studying the coordinated regulation of gene expression between linear genomic coordinates and three-dimensional spatial structures. HiBrowser allows for the superposition of two Hi-C heatmaps and offers various comparison modes such as A/B, B/A, and AMB, enabling visual comparative analysis of chromosomal spatial structures. HiBrowser also provides a cloning mode that allows for the synchronous display of genomic coordinates or the same region associated with the same or different reference genomes of multiple samples on the same visualization page, providing an efficient visualization tool for studying species diversity and sample variations. In comparative analysis of homologous species, HiBrowser supports the synchronous browsing of the same gene coordinates in closely related species, allowing users to import corresponding multi-omics annotation tracks and three-dimensional spatial structure information to provide a three-dimensional perspective on regulatory patterns that linear genomic coordinates alone cannot fully explain. For example, It has found the similar TAD structures and chromosomal loops near the BCL6 gene in the mouse and human genomes. Additionally, HiBrowser provides an interactive dynamic 3D chromatin simulation model that is synchronized with Hi-C heatmaps. It supports precise searching of relevant data for distal cis-regulatory elements(cREs) and allows users to navigate to any region of interest on the Hi-C heatmap based on the search results.