Predicting and visualizing vertebrate genome duplication database
Aug 01,2022 Editor:Centre for Bioinformatics and Intelligent Medicine
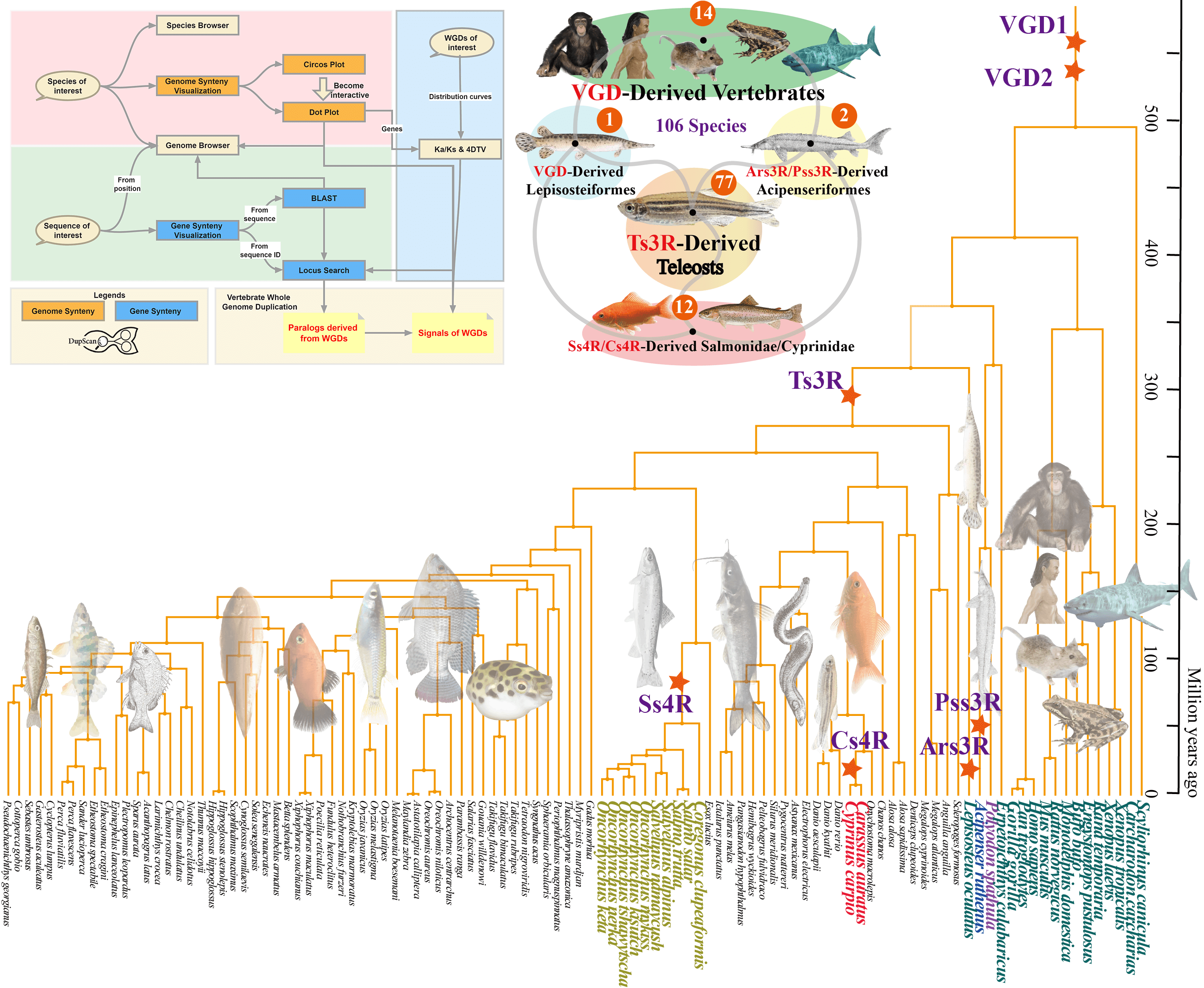
Duplicated genes prevail in vertebrates and are important in the acquisition of new genes and novelties. They have greatly characterized the foundation of genome evolution. Whole genome duplication (WGD) is one of the sources of duplicated genes and is also the most dramatic process among all duplication events. WGDs provide raw materials for natural selection by increasing the flexibility and complexity of the genome. WGDs are the driving force for the evolution of vertebrates and contribute greatly to their species diversity. Here, we constructed the DupScan database (https://dupscan.sysumeg.com/) by integrating 106 chromosomal-level genomes, which can analyze and visualize synteny at both the gene and genome scales, visualize the Ka, Ks, and 4DTV values, and browse genomes. DupScan was used to perform functional adaptation for the intricate WGD investigation based on synteny matching. DupScan is a database for visualizing and predicting vertebrate synteny and genome duplication. It provides specialized functions to analyse the computation-consuming WGD (Whole Genome Duplication) events by visualizing macro-synteny/micro-synteny, chromosome structures, gene/gene family evolution pattern, Ka/Ks/4DTV distributions. DupScan serves as a one-stop analysis platform for synteny and WGD research in which users can analyze and predict synteny and WGD patterns across 106 species of whole genome sequences. This further aided us in elucidating genome evolutionary patterns across over 60,000 vertebrate species with synteny and WGD events.